Tableau Server (Collector method) - v2.0.0
About Collectors
Collectors are extractors that are developed and managed by you (A customer of K).
KADA provides python libraries that customers can use to quickly deploy a Collector.
Why you should use a Collector
There are several reasons why you may use a collector vs the direct connect extractor:
You are using the KADA SaaS offering and it cannot connect to your sources due to firewall restrictions
You want to push metadata to KADA rather than allow it pull data for Security reasons
You want to inspect the metadata before pushing it to K
Using a collector requires you to manage
Deploying and orchestrating the extract code
Managing a high water mark so the extract only pull the latest metadata
Storing and pushing the extracts to your K instance.
Pre-requisites
Python 3.6 - 3.10
Tableau Server Version [2019.3] and above.
Enable the Tableau Metadata API for Tableau Server
This requires a server restart if not enabled
Tableau API access
An API user (record the username and password) needs to be created to access Tableau API.
The user cannot be a SSO user. This is a Tableau limitation. SSO users cannot access Tableau API https://help.tableau.com/current/api/rest_api/en-us/REST/rest_api_concepts_auth.htm
User needs
Site Administrator CreatororServer/Site Administratorrole. Roles are dependent on both Licensing and Server version see https://help.tableau.com/current/server/en-us/users_site_roles.htmSite Administrator Creatoris only available on Role Based Licensing ModelServer/Site Administratoris available on both Role Based and Core Based Licensing Model
Tableau Repository access
Follow the instructions to create a user that can access the Tableau repositoryhttps://help.tableau.com/current/server/en-us/perf_collect_server_repo.htm
This requires a server restart if not enabled
Note the Tableau repository default user is called
readonly
Access to K landing directory.
Step 1: Create the Source in K
Create a Tableau source in K
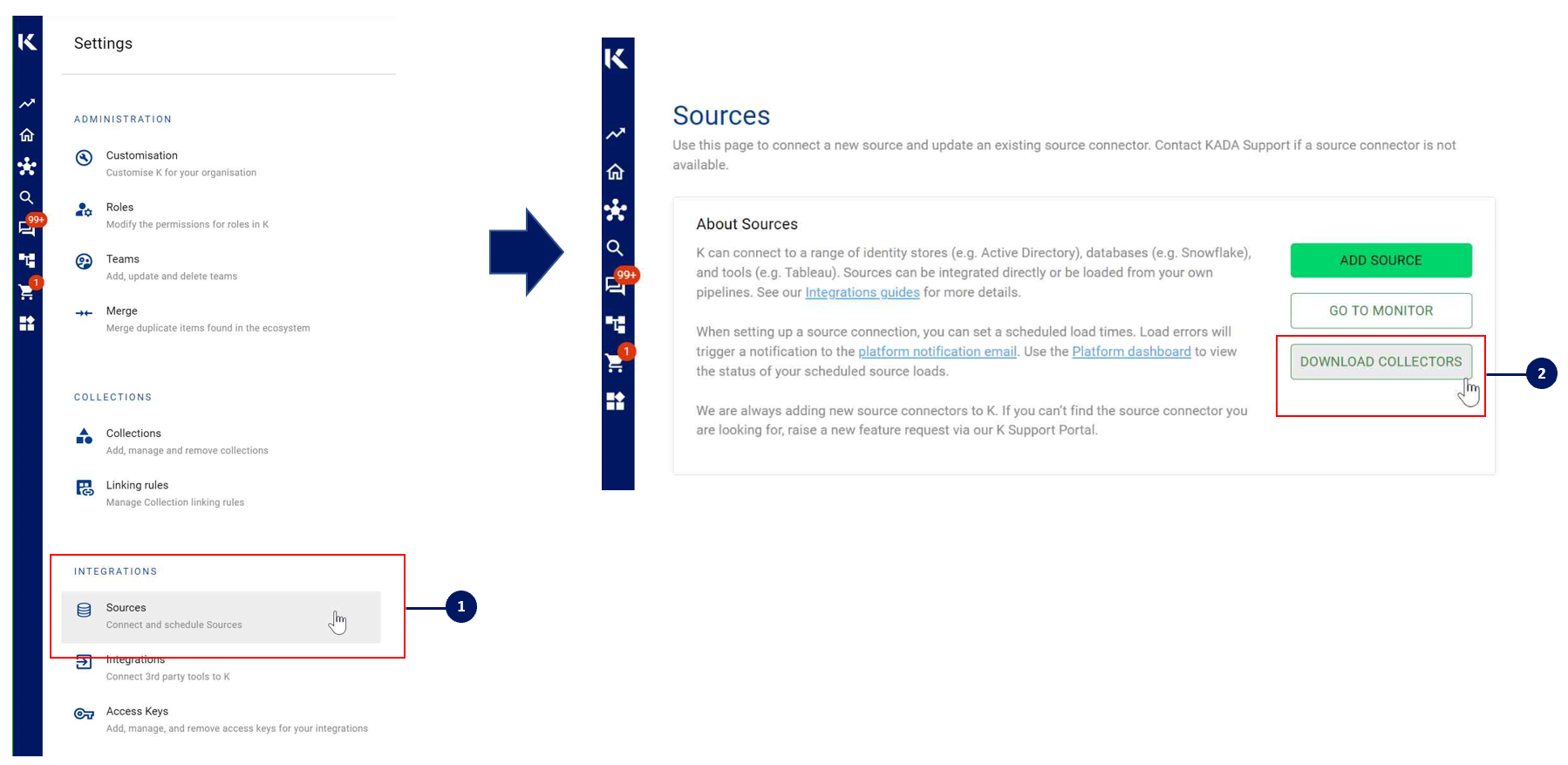
Go to Settings, Select Sources and click Add Source
Select “Load from File” option
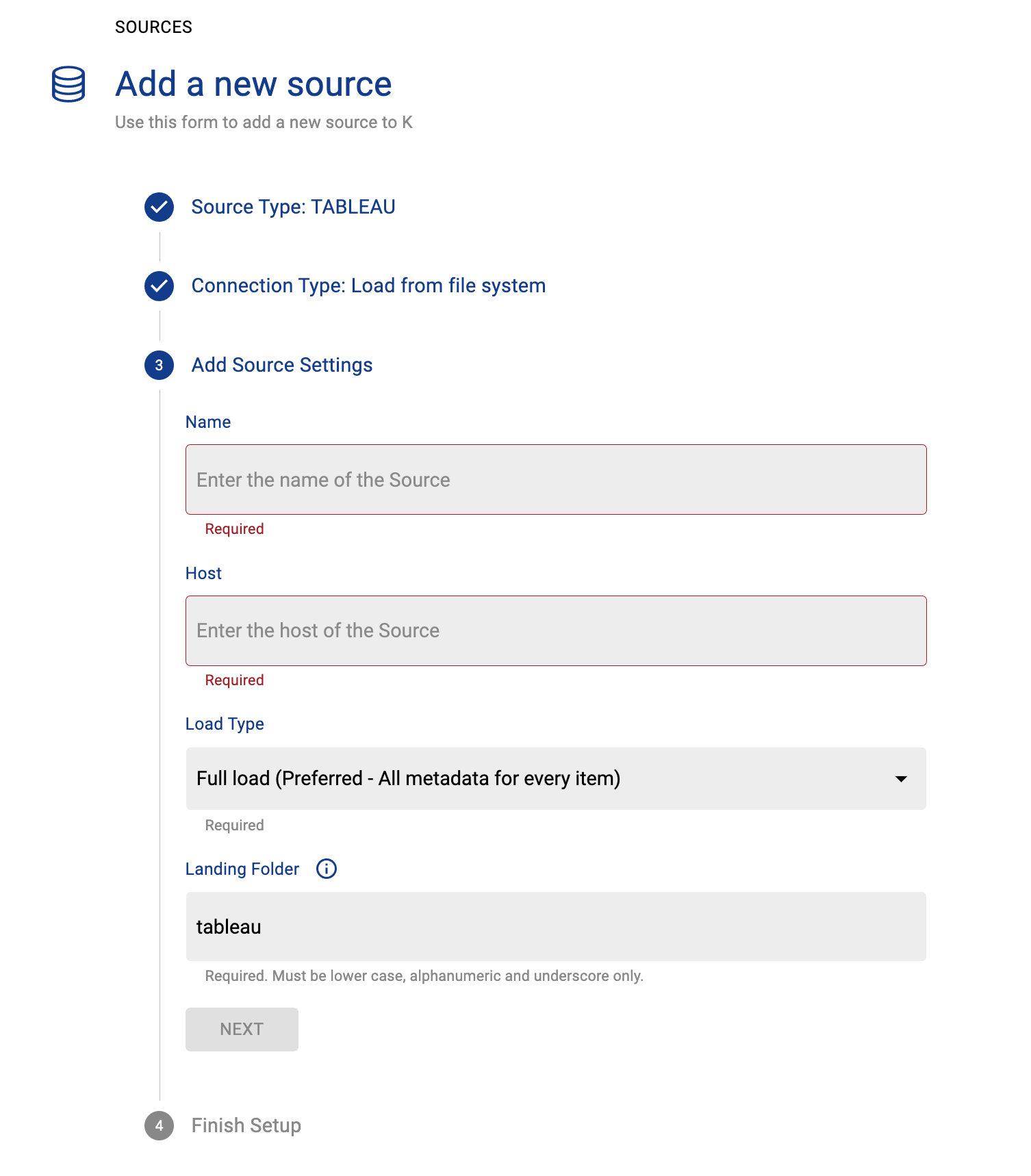
Give the source a Name - e.g. Tableau Production
Add the Host name for the Tableau server
Click Finish Setup
Step 2: Getting Access to the Source Landing Directory
When using a Collector you will push metadata to a K landing directory.
To find your landing directory you will need to
Go to Platform Settings - Settings. Note down the value of this setting
If using Azure: storage_azure_storage_account
if using AWS:
storage_root_folder - the AWS s3 bucket
storage_aws_region - the region where the AWS s3 bucket is hosted
Go to Sources - Edit the Source you have configured. Note down the landing directory in the About this Source section
To connect to the landing directory you will need
If using Azure: a SAS token to push data to the landing directory. Request this from KADA Support (support@kada.ai)
if using AWS:
an Access key and Secret. Request this from KADA Support (support@kada.ai)
OR provide your IAM role to KADA Support to provision access.
Step 3: Install the Collector
It is recommended to use a python environment such as pyenv or pipenv if you are not intending to install this package at the system level.
Some python packages also have dependencies on the OS level packages, so you may be required to install additional OS packages if the below fails to install.
You can download the Latest Core Library and whl via Platform Settings → Sources → Download Collectors
Run the following command to install the collector
pip install kada_collectors_extractors_tableau-2.0.0-py3-none-any.whlStep 4: Configure the Collector
The collector requires a set of parameters to connect to and extract metadata from Tableau.
PARAMATER | TYPE | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|---|
server_address | string | Tableau server address inclusive of http/https | |
username | string | Username to log into tableau api | “tabadmin” |
password | string | Password to log into tableau api |
|
sites | list<string> | List of specific sites that you wish to extract, if left as [] it will extract all sites. | [] |
db_host | string | This is generally the same as server address less the http/https | “10.1.19.15” |
db_username | string | By default the tableau database use is readonly should not need to change this unless you actively manage the database | “readonly” |
db_password | list<string> | Password for the database user |
|
db_port | integer | Default is 8060 unless your tableau is configured differently | 8060 |
db_name | string | Default database to use is workgroup | “workgroup” |
meta_only | boolean | If for some reason you want to extract meta only set this to true otherwise leave it as false | false |
retries | integer | Number of retries that the extractor should hit the API incase of intermittent failures, default is 5 | 5 |
dry_run | boolean | By doing a dry run you produce the mapping.json file which is used to populate the mapping field below. It is recommended you do a dry run first to see what databases are available to map. | true |
output_path | string | Absolute path to the output location where files are to be written | “/tmp/output” |
mask | boolean | To enable masking or not | true |
mapping | json | This should be populate with the mapping.json output where each data source name mentioned is mapped to an onboarded K host | Where analytics.adw is the onboarded database in K
CODE
|
These parameters can be added directly into the run or you can use pass the parameters in via a JSON file. The following is an example you can use that is included in the example run code below.
kada_tableau_extractor_config.json
{
"server_address": "",
"username": "",
"password": "",
"sites": [],
"db_host": "",
"db_username": "readonly",
"db_password": "",
"db_port": 8060,
"db_name": "workgroup",
"meta_only": false,
"retries": 5,
"dry_run": false,
"output_path": "/tmp/output",
"mask": true,
"mapping": {}
}Step 5: Run the Collector
The following code is an example of how to run the extractor. You may need to uplift this code to meet any code standards at your organisation.
This can be executed in any python environment where the whl has been installed.
This code sample uses the kada_tableau_extractor_config.json for handling the configuration details
import os
import argparse
from kada_collectors.extractors.utils import load_config, get_hwm, publish_hwm, get_generic_logger
from kada_collectors.extractors.tableau import Extractor
get_generic_logger('root') # Set to use the root logger, you can change the context accordingly or define your own logger
_type = 'tableau'
dirname = os.path.dirname(__file__)
filename = os.path.join(dirname, 'kada_{}_extractor_config.json'.format(_type))
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='KADA Tableau Extractor.')
parser.add_argument('--config', '-c', dest='config', default=filename, help='Location of the configuration json, default is the config json in the same directory as the script.')
args = parser.parse_args()
start_hwm, end_hwm = get_hwm(_type)
ext = Extractor(**load_config(args.config))
ext.test_connection()
ext.run(**{"start_hwm": start_hwm, "end_hwm": end_hwm})
publish_hwm(args.name, end_hwm)Advance options:
If you wish to maintain your own high water mark files elsewhere you can use the above section’s script as a guide on how to call the extractor. The configuration file is simply the keyword arguments in JSON format. Refer to this document for more information Collector Integration General Notes | Storing-HWM-in-another-location
If you are handling external arguments of the runner yourself, you’ll need to consider additional items for the run method. Refer to this document for more information Collector Integration General Notes | The-run-method
Step 6: Check the Collector Outputs
K Extracts
A set of files (eg metadata, databaselog, linkages, events etc) will be generated. These files will appear in the output_path directory you set in the configuration details
High Water Mark File
A high water mark file is created in the same directory as the execution called tableau_hwm.txt and produce files according to the configuration JSON. This file is only produced if you call the publish_hwm method.
from kada_collectors.extractors.tableau import Extractor
kwargs = {my args} # However you choose to construct your args
hwm_kwrgs = {"start_hwm": "end_hwm": } # The hwm values
ext = Extractor(**kwargs)
ext.run(**hwm_kwrgs)class Extractor(server_address: str = None, username: str = None, password: str = None, \
sites: list = [], db_host: str = None, db_password: str = None, \
db_port: int = 8060, db_name: str = '≈', db_username: str = 'readonly', \
meta_only: bool = False, events_only: bool = False, retries: int = 5, \
dry_run: bool = False, output_path: str = './output', \
mask: bool = False, mapping: dict = {})server_address: server address
username: username to sign into server
password: password to sign into server
sites: list of sites to extract.
db_host: Tableau database address
db_password: Tableau database password
db_port: Tableau database port
db_name: Tableau database name
db_username: Tableau database username
meta_only: extract metadata only
events_only: extract events only
retries: Number of attemps if an API fails on NonXMLResponse Error, default is 5
dry_run: If specified the extractor will do a dry run to produce a template mapping.
output_path: full or relative path to where the outputs should go
login_timeout: The timeout for snowflake Auth
mask: To mask the META/DATABASE_LOG files or not
Step 7: Push the Extracts to K
Once the files have been validated, you can push the files to the K landing directory..
You can use Azure Storage Explorer if you want to initially do this manually. You can push the files using python as well (see Airflow example below)
Example: Using Airflow to orchestrate the Extract and Push to K
# built-in
import os
# Installed
from airflow.operators.python_operator import PythonOperator
from airflow.models.dag import DAG
from airflow.operators.dummy import DummyOperator
from airflow.utils.dates import days_ago
from airflow.utils.task_group import TaskGroup
from plugins.utils.azure_blob_storage import AzureBlobStorage
from kada_collectors.extractors.utils import load_config, get_hwm, publish_hwm, get_generic_logger
from kada_collectors.extractors.tableau import Extractor
# To be configed by the customer.
# Note variables may change if using a different object store.
KADA_SAS_TOKEN = os.getenv("KADA_SAS_TOKEN")
KADA_CONTAINER = ""
KADA_STORAGE_ACCOUNT = ""
KADA_LANDING_PATH = "lz/tableau/landing"
KADA_EXTRACTOR_CONFIG = {
"server_address": "http://tabserver",
"username": "user",
"password": "password",
"sites": [],
"db_host": "tabserver",
"db_username": "repo_user",
"db_password": "repo_password",
"db_port": 8060,
"db_name": "workgroup",
"meta_only": False,
"retries": 5,
"dry_run": False,
"output_path": "/set/to/output/path",
"mask": True,
"mapping": {}
}
# To be implemented by the customer.
# Upload to your landing zone storage.
def upload():
output = KADA_EXTRACTOR_CONFIG['output_path']
for filename in os.listdir(output):
if filename.endswith('.csv'):
file_to_upload_path = os.path.join(output, filename)
AzureBlobStorage.upload_file_sas_token(
client=KADA_SAS_TOKEN,
storage_account=KADA_STORAGE_ACCOUNT,
container=KADA_CONTAINER,
blob=f'{KADA_LANDING_PATH}/{filename}',
local_path=file_to_upload_path
)
with DAG(dag_id="taskgroup_example", start_date=days_ago(1)) as dag:
# To be implemented by the customer.
# Retrieve the timestamp from the prior run
start_hwm = 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:SS'
end_hwm = 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:SS' # timestamp now
ext = Extractor(**KADA_EXTRACTOR_CONFIG)
start = DummyOperator(task_id="start")
with TaskGroup("taskgroup_1", tooltip="extract tableau and upload") as extract_upload:
task_1 = PythonOperator(
task_id="extract_tableau",
python_callable=ext.run,
op_kwargs={"start_hwm": start_hwm, "end_hwm": end_hwm},
provide_context=True,
)
task_2 = PythonOperator(
task_id="upload_extracts",
python_callable=upload,
op_kwargs={},
provide_context=True,
)
# To be implemented by the customer.
# Timestamp needs to be saved for next run
task_3 = DummyOperator(task_id='save_hwm')
end = DummyOperator(task_id='end')
start >> extract_upload >> end